This is the 8th exercise of practicepython.
Remember the rules:
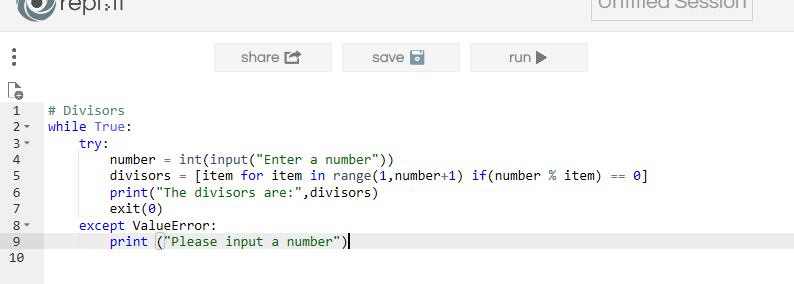
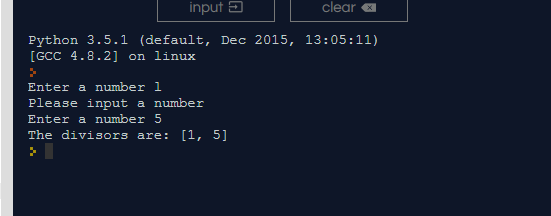
Output 1:

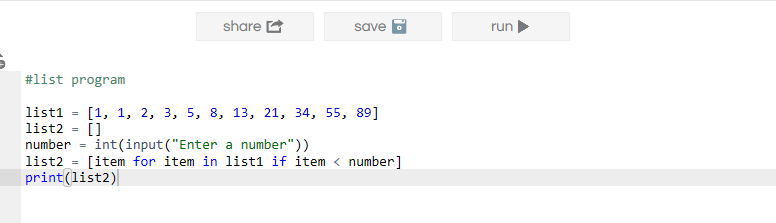
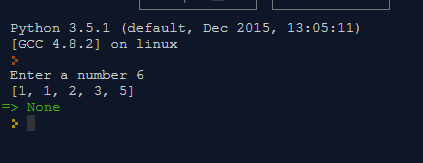
Output 2:

GitHub Reference:
https://gist.github.com/pinkpretty/e648c67ba012fc09d0fb963b0a249acc
Happy Coding ! :)
Exercise:
Make a two-player Rock-Paper-Scissors game. (Hint: Ask for player plays (usinginput), compare them, print out a message of congratulations to the winner, and ask if the players want to start a new game)Remember the rules:
- Rock beats scissors
- Scissors beats paper
- Paper beats rock
Output 1:

Output 2:

GitHub Reference:
https://gist.github.com/pinkpretty/e648c67ba012fc09d0fb963b0a249acc
Happy Coding ! :)